
When you install Workstation Pro on a Windows or Linux host system, a bridged network (VMnet0) is set up for you. If the host system is on a network, bridged networking is often the easiest way to give the virtual machine access to that network. Bridged Networkingīridged networking connects a virtual machine to a network by using the network adapter on the host system. You can also use the virtual networking components to create sophisticated custom virtual networks. Then select the type of MAC address and click Add … virtual MAC address.You can configure bridged networking, NAT, and host-only networking for virtual machines. The virtual MAC configuration displays.Ĭlick the cogwheel next to the IP address you want to configure.

The advanced configuration displays.Ĭlick Add virtual MAC. Scroll down to the network configuration section and click + Info next to the failover IP you want to configure. Select the server you want to configure and click Manage. How to add a virtual MAC addressĬlick Server > Server list to display a list of your physical machines. With this configuration, no virtual MAC addresses are required. Only the MAC address of your physical network card is broadcasted on the network. Your physical server and its virtual machines are seen as one single server. You share the same IP address for all your virtual machines with a NAT configuration. You can add virtual MAC addresses known and allowed on the network to solve this problem.
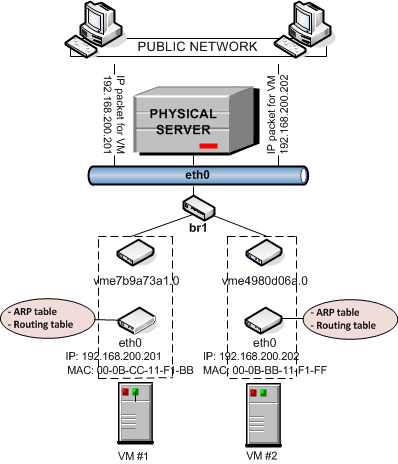
If you start a virtual machine in bridge mode, protection will be activated on the switch, and your network port will be closed. In bridge mode, the network equipment sees your server and your virtual machines as different servers.įor security reasons, no other network equipment is allowed on our network, except for the MAC address of your physical network card. In general two connectivity modes are possible for the networking of virtual machines:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
